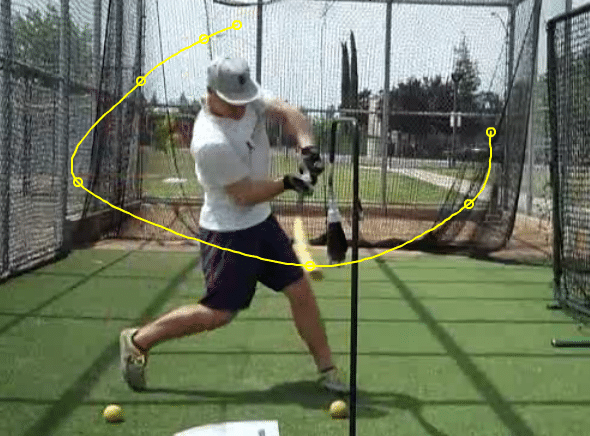
Bust bat drag hitting experiment featuring JD Martinez! Discover how to fix a disconnected swing and get rid of dragging back elbow with the scap load for baseball or softball hitters. Do “Ball Under Back Arm Drills” build a quick swing?
In my humble opinion, NO. Unless, and in the case of curing bat drag, the hitter is pinching the rear scapula in towards the spine with the ball underneath the back arm. But then again, for that, why would you want the ball there in the first place? A quick and consistently powerful swing comes from taking ALL slack out of the system, and the scap load is part of that formula.
Boost “Top Out” Bat Speed By “Hiding The Hands”, Like JD Martinez…
Question: Does Hiding the Hands Increase Bat Speed versus NOT Hiding Them?
Using the Zepp (Labs) Baseball app, I wanted to use the Scientific Method to analyze if hiding the hands from the pitcher prior to stride landing boosts bat speed, over not hiding them. Some may call this the “Scap Row”.
And we’ll see what proper baseball hitting mechanics look like with MLB Player of the Week (July 6th) JD Martinez of the Detroit Tigers.
My intern for the summer, red-shirt college freshman Tyler Doerner did the experiment.
Background Research
Most hitting instructors may call this the Scapula Row, or Scap Row for short. “Hiding the hands” is essentially the same thing, but is a much more sticky coaching cue.
“Hiding the Hands” has to do with loading the springy fascial material in the body. Without this springy fascia your bones and muscles would drop to the ground. It’s what gives muscles their shape, and what the bones and muscles ‘float’ in, according to Thomas Myers in his book Anatomy Trains.
“Hiding the Hands” also allows a hitter to be in proper baseball hitting mechanics to achieve high angular velocity early in the turn. This has to do with the Conservation of Angular Momentum. Achieving high angular velocity, early in the turn, is critical to Time To Impact and covering more plane of the pitch with the barrel.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
Hypothesis
Based on the above research, I think proper baseball hitting mechanics, a la “Hiding the Hands”, from the pitcher (pre-turn) will have a big impact on bat speed versus not hiding them. I think results will be similar to what the “Showing the Numbers” Experiment revealed, where we saw an average bat speed increase of 6-mph over 200 swings.
Proper Baseball Hitting Mechanics: JD Martinez “Hiding Hands” Experiment
Equipment Used:
- Zepp Baseball app
,
- Solohitter (like the SwingAway which I like better),
- Camera Phone, Coaches Eye app,
and Tripod, and
- 33 inch, 30 ounce wood bat.
Setup:
- Forward momentum was eliminated in this experiment, and hitting from a 1-2 second pause at landing
- First 100 baseballs were hit “NOT Hiding the Hands”
- Second 100 baseballs were hit “Hiding the Hands”
- There was no break between tests because Tyler was trying to beat the rains coming
Data Collected (Zepp Baseball App):
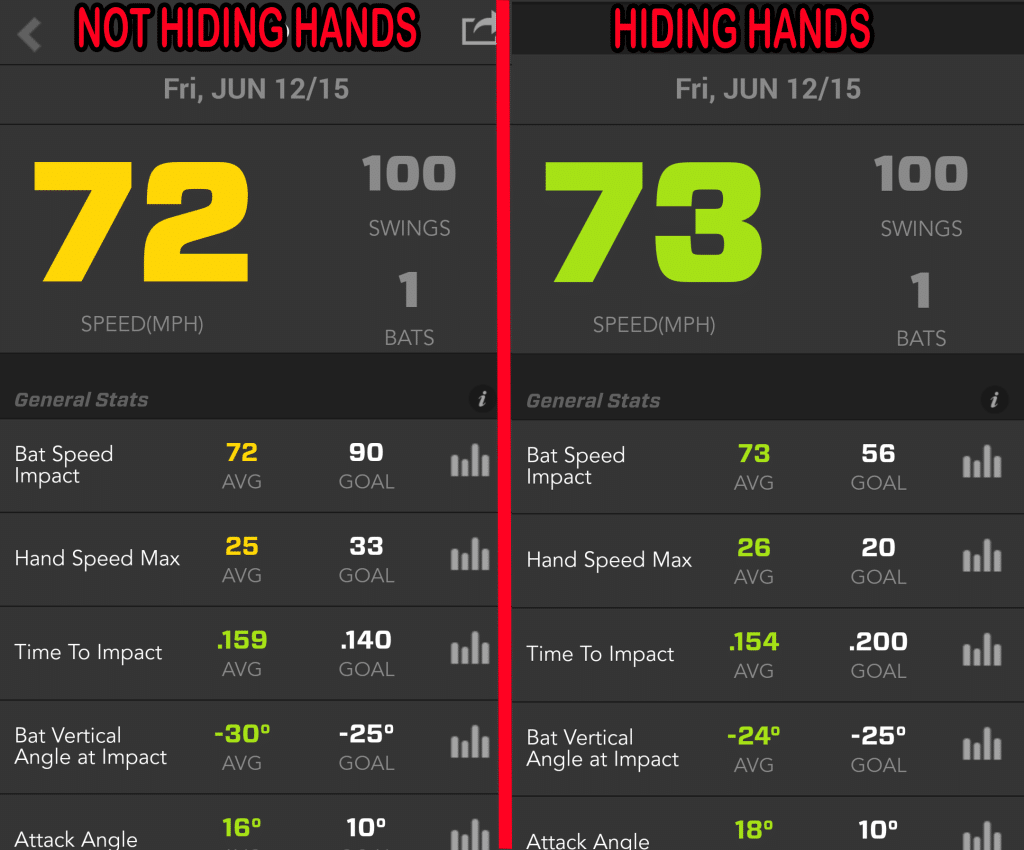
In this proper baseball hitting mechanics “Hiding the Hands” Zepp Experiment, see how “Hiding the Hands” slightly won out in Bat & Hand Speed, and Time to Impact rather than “Not Hiding the Hands”…
Data Analysis & Conclusion
- As you can see, “Hiding the Hands” beat almost every category…
- On average, 1-mph change in Bat Speed,
- On average, 1-mph change in Hand Speed, and
- On average, .005 change in Time To Impact.
“Hiding the Hands” didn’t have a significant jump in bat and hand speed, or Time To Impact than “NOT Hiding the Hands.” But there was a difference in top-out bat speeds:
- Top-4 “Hiding the Hands” bat speeds (in mph): 85, 84, 84, and 82.
- Top-4 “Not Hiding the Hands” bat speeds (in mph): 82, 81, and the rest were less than 79.
So, top out bat speed increased by 3-mph, and there were consistent higher bat speeds with “Hiding the Hands”.
Notes
- The results of the proper baseball hitting mechanics “Hiding the Hands” Zepp Experiment may have been skewed because Tyler didn’t take a break between tests.
- The following experiments will be using what one of my readers and motor learning and performance researcher Brad McKay suggests, which is counterbalancing the experiment. Essentially it’s breaking experiment swings into 25 swing blocks, and ordering them a certain way. For example, “Hiding the Hands” would be block “A”, and “Not Hiding the Hands” would be block “B”. The 200 swings would be broken into 8 blocks and ordered accordingly: ABBA BAAB. As Brad McKay says, “The issue with not counterbalancing is that you don’t actually know the effect of time because it is confounded with condition. In other words, you might always do better on the second block of 100 because of a warm-up decrement or a practice effect.” Thank you Brad for the experiment tip! We’ll do better next time 😀
- About JD Martinez…this FanGraphs.com link titled, “JD Martinez on His Many Adjustments” is a great example of players today opening their eyes to how the body really moves, and not what some talking head thinks. Basically, JD Martinez subscribed to swinging “down on the ball” until he got injured in 2014, I believe. Then he started analyzing teammates’ and opponents’ swings that were crushing the ball, and found out they weren’t swinging down at all.
- A week or two after the 2015 All Star break, according to FanGraphs.com, JD Martinez had 27 homers. His season high before that? 23, in 2014. To me, JD Martinez is a big slugger at 6’3″, 220-pounds. But when big sluggers do small slugger things (like being more effective with mechanics), even bigger things can happen. JD Martinez does a great job of “Showing his Numbers” and “Hiding the Hands”. This compresses the springy fascia material in the body.
The Bottom Line?
In this proper baseball hitting mechanics “Hiding the Hands” Zepp Swing Experiment, “Hiding the Hands” doesn’t seem to give a hitter a significant jump in Bat and Hand Speed, or Time to Impact. But definitely an increase nonetheless. But what using proper baseball hitting mechanics, like “Hiding the Hands”, does appear to do, is boost top-out bat speeds. AND, make those top-out bat speeds repeatable.