Is Hitting For Power: Hips Before Hands, Hip Rotation, Legs, Or Lower Body Mechanics For Youth Baseball & Softball Swing? | Drills To Do At Home
Learn whether hitting for power is either or neither of: hips before hands, hip rotation, all in the legs, or lower body mechanics. You’ll discover useful youth baseball and softball swing drills to do at home.
Zepp Swing Experiment Attempting To Put Value On Role Of Pelvis In Swing
Question: How Much Does Pelvis Add to Bat Speed at Impact?
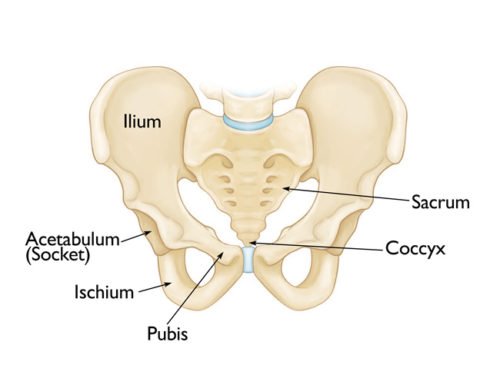
According to InnerBody.com, the pelvis is a sturdy ring of bones that protects the delicate organs of the abdomino-pelvic cavity while anchoring the powerful muscles of the hip, thigh, and abdomen. Several bones unite to form the pelvis, including the sacrum, coccyx (tail bone), and the left and right coxal (hip) bones. Photo courtesy: OrthoInfo.aaos.org
Using the Zepp (Labs) Baseball app, I wanted to employ the Scientific Method to analyze how much turning the pelvis (some refer to this as the hips) adds to Bat Speed at Impact. The ‘Front Facing Swings’ are an attempt to isolate out the role of the pelvis in the swing, so we can analyze how much the pelvis adds to swing performance.
Just a heads up, the “pelvis” and “hips” are not the same thing. The hips are a small part of the pelvis. However, most coaches refer to “hips” when instructing the swing, when most likely they mean “pelvis”.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
Background Research
For those coaches with a Growth Mindset that want to find out more about the science of locomotion. I’d recommend reading the following technical books:
- Anatomy Trains
by Thomas Myers, and
- The Spinal Engine
by Dr. Serge Gracovetsky.
If working through the weeds isn’t for you, then you can click the following HPL posts that synthesize the information contained in the previously mentioned books:
- David Weck Interview: More Speed, Control, & Power With LESS Wear And Tear On The Body
- Josh Donaldson: Stay Closed & ADD Bat & Ball Exit Speed
- Roger Federer + Pitch Mechanics = Repeatable Power (Hitting Video)
I’ve done two swing experiments revealing the role of the shoulders in the swing that tested the value of ‘Showing Numbers’ versus ‘NOT’. These showed an average increase to Bat Speed at Impact – Showing Numbers – of between 5 to 6-mph. In addition, one of the experiments showed an average increase to Ball Exit Speed of over 9-mph ‘Showing Numbers’! That’s between 38 to 48-feet of ADDED batted ball distance by ‘Showing Numbers’:
- Want To ADD Between 38.44 & 48.05-mph Of Batted Ball Distance?
- Buster Posey Video: Not ALL In The Hips? [Experiment]
This Zepp swing experiment is attempting to put value on the role of the pelvis in the swing.
Hypothesis
Ted Williams, in his book The Science Of Hitting, said the ‘hips lead the way’. This observation is irrefutable when watching slow motion video of elite hitters. A majority of coaches teach primarily a ‘hips only’ strategy, which I disagree with. I feel ‘firing the hips’ is over-taught and over-valued, while the role of the shoulders is under-taught and under valued. The objective of this experiment is to see what benefit the pelvis (or hips) add to swing performance.
I predict ‘Regular Swings’ will have a substantial increase in Bat Speed at Impact than the ‘Front Facing Swings’.
Performance Benefit of Pelvis Swing Experiment
Equipment Used:
- Zepp Baseball app (to measure Bat Speed, Hand Speed, Time to Impact, & Attack Angle),
- Backspin batting tee,
- Two yellow dimple baseballs (feedback markers),
- Flip camera
to record swings, and
- 33 inch bamboo bat.
Setup:
- Yellow dimple ball feedback markers to keep starting footwork the same = bat length…I used two yellow dimple ball markers to make my stance setup consistent. One was placed inside my back foot, close to the plate. The other was placed one bat’s length ahead of the back marker.
- Tee was set one baseball’s length behind the front feedback marker, and tee height was about mid-thigh
- We stayed as consistent as we could with keeping the ball height and depth the same for most swings.
- The two tests in the swing experiment were counter-balanced. Which consisted of eight blocks of 25-swings done in the following order ABBA BAAB. ‘Front Facing Swing’ was letter ‘A’, and ‘Regular Swing’ was letter ‘B’. 200 total swings were completed in the experiment, 100 per test. Counter-balancing helps remove the “getting tired” and “warm up” factors.
- The objective of ‘Front Facing Swings’ was to start the ‘belt buckle’ pointing at the pitcher, and to minimize pelvic movement.
- Experiment Day-1 on 6/19 we completed 75 total swings (25 ‘Front Facing’ & 50 ‘Regular’). Experiment Day-2 on 6/26 we completed 125 swings (75 ‘Front Facing’ & 50 ‘Regular’).
- We had to break the 200 total swings into two days, with the second day coming 1 week later, because of time constraints.
Data Collected (Zepp Baseball App):
‘Front Facing Swings’ Days 1 & 2 side by side…
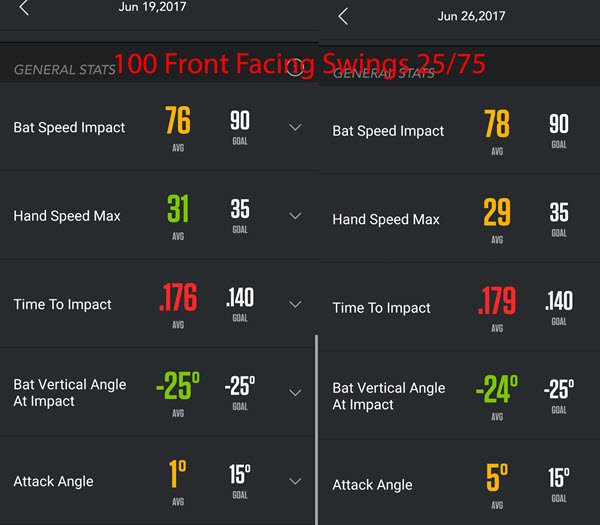
‘Front Facing Swing’ AVERAGES for the following metrics: 77-mph Bat Speed at Impact, 30-mph Hand Speed Max, 0.177-secs Time To Impact, -24.5* Bat Vertical Angle at Impact, & 3* Attack Angle.
‘Regular Swings’ Days 1 & 2 side by side…
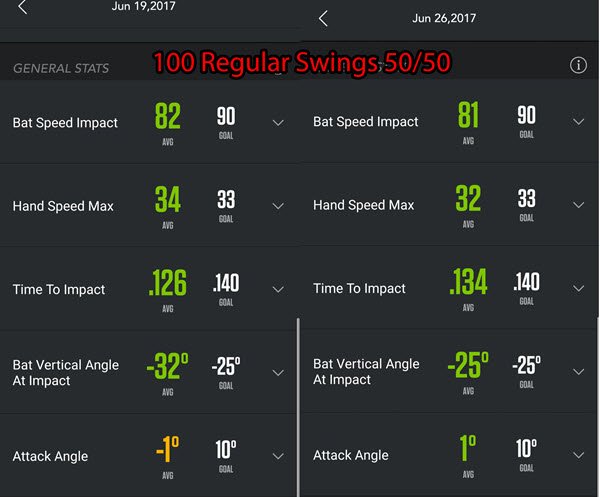
‘Regular Swing’ AVERAGES for the following metrics: 81.5-mph Bat Speed at Impact, 33-mph Hand Speed Max, 0.130-secs Time To Impact, -28.5* Bat Vertical Angle at Impact, & 0* Attack Angle.
Data Analysis & Conclusion
Zepp data analysis comparing the averages of averages:
- 4.5-mph INCREASE to Bat Speed at Impact in ‘Regular Swings’,
- 3-mph INCREASE to Hand Speed Max in ‘Regular Swings’,
- 0.047 DECREASE to Time To Impact in ‘Regular Swings’,
- -4-degree DECREASE to Bat Vertical Angle at Impact in ‘Regular Swings’, and
- -3-degree DECREASE to Attack Angle in ‘Regular Swings’.
Notes
- The increase in Bat Speed at Impact and Hand Speed Max confirmed my hypothesis, and didn’t surprise me since the first piece of The Spinal Engine
to interact with Gravitational Forces is the pelvis.
- It’s also interesting to note, that you can see from the side-by-side video of the swing, that I wasn’t able to keep the “belt buckle” ‘front facing’ as much as I would have liked to on ‘Front Facing Swings’, so possibly the pelvis could have added a bit more. I was feeling inside right knee tightness when forcing pelvis to stay facing forward.
- The DECREASE in Time To Impact with ‘Regular Swings’ could have been due to the increased step and/or unfamiliarity with the movement, while doing ‘Front Facing Swings’.
- In past swing experiments testing ‘Down Shoulders’ and ‘Showing Numbers’ I increased my Attack Angle – in the positive. I think the 3-degree increase in positive Attack Angle for ‘Front Facing Swings’ was due to better execution of those elements.
- We were testing Ball Exit Speed in the beginning but had equipment malfunction (batteries went dead). I was too many swings in when the equipment was fixed, so we threw BES out in this experiment. I’d love to see BES measured in a future review of this swing experiment.
- One last thought, because my pelvis inwardly turned toward the catcher – drastically – on ‘Front Facing Swings’, we saw quite a drop-off in production. Does this give evidence that an inward turn before the swing may be inferior to keeping the pelvis in neutral (or belt bucket facing plate)?
- Best Youth Baseball Hitting Program to Boost Rotational Power Fast—Trusted by MLB’s Rajai Davis & Built on the Catapult Loading System - June 22, 2025
- The #1 Arm Care Program for Youth Baseball: Why Top Travel Coaches Trust Jaeger’s J-Bands & Long Toss Routine to Prevent Injury Fast - June 3, 2025
- Are Baseball Hitting Lessons Worth It in 2025? Fix Your Kid’s Swing Fast With Pro-Approved Drills (Before You Waste Another $60) - May 29, 2025












Joey,
Since you are referencing Ted Williams’ THE SCIENCE OF HITTING, do an experiment comparing “regular swings” with swings taken with the pelvis restricted as pictured in Ted’s book on page 52.
Joe, that’s on the swing experiment bucket list, using sideways back foot 😀
Joey,
The experiment you posted on December 16, 2016 did just that.
Totally Joe.