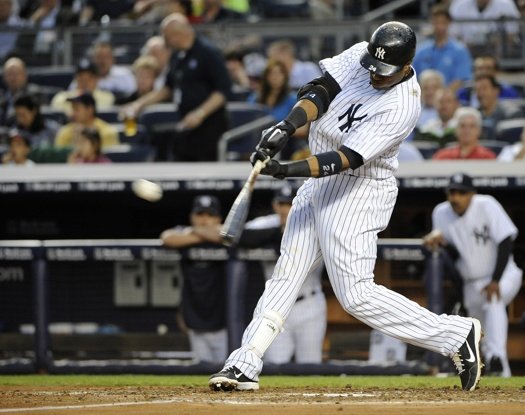
Discover faster bat speed drills to improve youth power hitting for baseball and softball mechanics. Learn how in this Francisco Lindor swing breakdown…
Francisco Lindor Swing Breakdown
Hey, what’s going on? It’s Joey Myers from the Hitting Performance Lab. In this Francisco Lindor swing breakdown video, we’re going to go over three different things…
- The first thing we’re going to do is are going to look at his metrics according to fan graphs,
- The next thing is the big three in the Catapult Loading System, and
- And then the last thing we’re going to look at is when the wrist snap happens…
Francisco Lindor Swing Breakdown: the Metrics
Now, let’s take a look at some of the stats and give a little context to this Francisco Lindor swing breakdown. You can see he is a smaller hitter, smaller slugger, 5-foot, 11-inches, 190-pounds. He switch hits.
You can see down here in 2019, putting his power in perspective… He’s hit 32 homers in the last years prior, 38, 33. That was 2017. And the video analysis swings we’ll look at in this video are from 2017. He’s hit about 40 doubles or so in those last three years or the last four years. 30 doubles in 2016, and hits about .284.
And if we look at his batted ball totals as in line drive percentage, ground ball percentage and fly ball percentage…line drive percentage in 2019 was just about average – 20 percent is league average – ground-ball rate is average, league average is 43%. Fly ball percentage is just slightly below average at 36.6%. Average is about 37%, but pretty close to league averages there.
The one thing that is above well above league average is his homerun to fly ball percentage, which is 17.4%. And you can see the prior year 17.3, then 14.0, then 9.9, and 13.0 are all well above average on the 9 or 9.5% of homerun to fly ball ratios as the major league average.
So let’s start with the big three in the Catapult Loading System in this Francisco Lindor swing breakdown. You have the lefty at bat over here and the righty at bat over here. Let’s give a little context to these pitches in the at bats. This is the second one over here.
We’re going to look at the pitch speed, 88-mph. Some kind of breaking ball, maybe a slider, and this one he hit for home run into the right field bleachers or right center field bleachers, over here on the right his righty at bat.
He’s a little bit out in front. We have a 79-mph, probably a slider here. That he pulls in the five and a half hole.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
The Big-3: Catapult Loading System
OK, so what I referred to as the big three and the Catapult Loading System is the build more consistent power in a swing. There are three buckets. Two, our systems, the different systems we teach, that’s one of them.
The second one is the pitch plane domination system. And that’s all about how to hit more line drives and the reaction time mastery system, which is all about footwork, vision, tracking and timing.
This Francisco Lindor swing breakdown video, we’re going to be going over the first system, the power systems, the Catapult Loading System. I refer to the big three as “showing numbers”, “downward shoulder angle”, and “hiding the hands”.
What you’re going to see here, I have both of these swings synced up, on the left, the homer, on the right, the ball that he was a little bit out in front he pulled into the five and a half hole for a ground ball base hit.
“Showing Numbers”
You can see that if we rewind to the beginning. And just so you know, the camera angle in center field is slightly off center towards the left or left center. It’s in center, but slightly towards left. And that is going to show any kind of right-handed batter as showing their numbers more than the left. So just understand that this isn’t a complete apple to apples comparison, but you’ll still see the difference in their starting positions and their landing positions.
You can see here, you can’t see Francisco Lindor’s number really on the left, and you can start to make it out a little bit here on the right. Again, probably because of off centered camera in center field.
As the pitcher starts to get into the windup, gets ready to release the ball, you can start to see over here on the right … again, with our camera angle, you can see that #12, pretty clear as day at this point.
And what I want you to do is, again, with that skew with the camera, watch the pinstripe. If we put a dot in these spots, as you’ll see Lindor pull in more with the pelvis almost similar to the Javier Baez swing analysis that I did a few weeks ago, you saw Baez extremely turn that pelvis in. And my argument is that we don’t have to do that…
See here that that pinstripe you can’t see any more on the right side, but on the left side you can still see it. Again, we get a skewed camera angle, but it didn’t move quite as much on the left as it did on the right. So, this is something that Lindor actually doesn’t have to do and might be closing himself off just slightly. But nonetheless, you can see you can pretty much make out almost the full one in the two.
I used to teach showing numbers as showing both numbers are showing at least a number and a half, evolved it more to where we want to create neck pressure. If we create neck pressure, then the hitter should be showing their numbers. It’s more of an objective measure of showing numbers because every hitter is different. Their mobility in their neck is different.
In this Francisco Lindor swing breakdown, you can see his head really anchoring down for it in a tracking position and he’s moving his shoulder underneath his chin as far as he can, creating a wringing towel effect between his head and his shoulders. And he’s creating this neck pressure at the T1/C7 vertebrae in the spine, just like wringing a towel out. And he’s creating that neck pressure, which as a result will show his numbers.
And also, could be on the right side since he possibly is inward turning his pelvis a little bit more. It could be why he’s shown his numbers a little bit more besides the camera angle. So that is the first of the big three, showing numbers or creating neck pressure.
“Downhill Shoulders”
The second of the big three is the downhill or downward shoulder angle. It’s the hitter dipping their front shoulder down, creating this downhill shoulder angle that you can see with this back elbow in this Francisco Lindor swing breakdown. You can see his back elbow, if you create this line, not quite as much over here on the right, he doesn’t raise that elbow quite as much as on the left.
And granted, too… If you look at his at bats in fan graphs, he has a lot more at bats, probably 60 plus percent more on the left than he does on the right because he’s seeing probably more righties than he is lefty pitchers. So, you can see he’s probably little bit more grooved on the left anyway. And his power numbers show it. He’s got plenty of more homers on the left than he does on the right. But again, that reflects the amount of plate appearances as well.
He has this downward shoulder angle on the right. He’s not using his back elbow as much. We do use back elbow with the hitters to steer the shoulders down, but not all hitters will click with that. We’ll just tell those hitters that they seem to for telling him to raise the back shoulder at landing. Then what tends to happen is their hands start to balloon up and rise up. We don’t want the hands to get up past a certain height. We want to make sure that their hands are in it in a decent, more comfortable position around the shoulder height – back shoulder height to be able to launch from.
So, if the hitter is having a hard time by bringing that back elbow up, like you see Francisco Lindor over here on the left, then what we’ll tell the hitter to do is just lower the front shoulder.
He’s creating neck pressure, which is showing the number, this is a protraction of the front scapula for you movement nerds out there, you kinesiology nerds out there, and he is creating this downward shoulder angle so that his shoulders can actually flip.
You’ll see the front shoulder pop up in the back shoulder that’s up will go down as he gets to the swing here. You see a complete reversal of that. And we should see in the follow through, we should see a complete reversal again back to almost where his right shoulder on the left over here.
So this front one ends up, starts down, pops up, and then should end up back down again over the other shoulder. And the reverse is true. Over here on the right, we see the left shoulder start down, pops up, and then it should end up back down again, which you see here. That is a proper deceleration of the spinal engine.
“Hiding Hands”
The last piece of the big three is hiding the hands from the pitcher. So you can see the hands here from the left. You can see slightly the bottom hand on the right. And then you’re going to see those hands disappear. You’ll see them reappear back behind his head, on the right, on the left, not quite so much. You see them disappear behind his head. But again, we’re talking about a different camera angle here.
And some call this the scapula row or a rear scalp retraction for the kinesiology nerds back there. We should see both a protraction of the front scapula, which is showing the numbers/neck pressure.
And we should also see a retraction of the rear scapula. We see both. We do not, especially in hitters like Lindor, who are 5’11”, 190 pounds. We do not see the ones that hit for power anyway. We do not see them only retracting the rear scapula and not showing their numbers, or not using neck pressure. We see both.
It is very hard for a hitter the size of Francisco Lindor to hit 30 homers a year for the last three or four years, without showing numbers and just doing the rear scapula retraction.
Not going to happen.
So those are the big three as it is to the Catapult Loading System, showing numbers, downhill shoulder angle, and hiding the hands. Now let’s check out the wrist snap…
Wrist Snap
A lot of young hitters, what they tend to do and there’s quite a few hitting instructors out there that are teaching this deep barrel dump and to “chicken wing” with the front elbow, 90-degree bend as it comes through impact.
The problem is, and this is what I’m seeing with both the hitting instructors and the hitters of the hitting instructors, and even in some of my hitters, as we train this out of their swing is, they create a lot of space between their front arm and their chest as they’re coming through.
You can see this was the pitch that was middle in that Francisco Lindor hit a homerun on to right. You can see how tight he keeps this barrel, and we talk about the belly button catcher’s glove…
Imagine a catcher’s glove in line with the hitter’s belly button and a catcher’s glove in line with the hitters back foot. This is important when it comes to pitches middle in and middle up because we want to be knocking off those catcher’s gloves and not knocking off the real catcher’s glove was back here.
But you can see in this Francisco swing breakdown. You can see him, his barrel entering the attack zone at the back-foot catcher’s glove, he’s actually a little bit late here, he ends up speeding it up with his wrist snap.
But what you’re going to see is almost like there is a wall happening here… And he’s going to get to this wall… And his hands are going to stop moving forward.
What we see with young hitters is we’ll see these hands continue forward and they end up way out over here, chicken winging with the elbow and their arm, front arm drifting far away from their chest, which we don’t want to do if we want a proper transfer of body to barrel to ball force.
We’re going to see the best hitters will stop, their hands will stop moving forward at a certain point, which you see is right here. It’s like the hands hit a wall and we have a wall drill for this, a wall turn or a phone booth drill that we use to help the hitter out with this, plus a wrist snap position.
You see, as he releases into the back foot catcher’s glove, you’re going to see him pivot. Imagine a red laser coming out of the knob and you get a green laser coming out of the barrel of the bat. And we see at a point where he’ll flip it, he’ll flip the red laser for the green. But you see this wrist snapping. Some may call pronation.
As he gets through this ball and you’re going to see post impact … both arms get extended, full extension. Both arms. Power V. This isn’t the power V that was taught about a couple of decades ago to happen at impact, that’s not what we’re trying to do.
This is the power V that happens after impact, and with a proper transfer from body to barrel to ball we should see this passed impact. But it uses a combination of the big three of the Catapult Loading System and the wrist snap. At one point, the knob has to stop moving forward linearly and has to let the wrist snap and pronate with the top hand.
Make sure that we’re swinging smarter by moving better … Like this video … Subscribe to our YouTube channel … and before I let you go…