Learn how to swing a bat and hit a baseball or softball faster, farther, and harder EVERY TIME. Discover beginner practice at home hitting to increase bat speed, power, exit velocity, and how to hit the ball in a certain direction.
Hitting A Baseball: Discover The Secret Of Impact
Debating the intricacies of hitting a baseball (or softball) can be as bad as discussing religion or politics. This is why we look to proven human movement science first. Hitting a baseball NOT easy, but we can make it easier. It has a lot of failure built into the fabric. The objective of every coach, instructor, or parent should be to build as many “fail-safes” into the system as possible.
We’re going to explore the following, as they relate to impact:
- Perry Husband & Effective Velocity,
- 90-Degree Angle to the Spine Rule NOT True?
- University of Miami Study: The Biomechanics of the Baseball Swing
- Conclusion…
First I want to start by setting the table…
Perry Husband & Effective Velocity
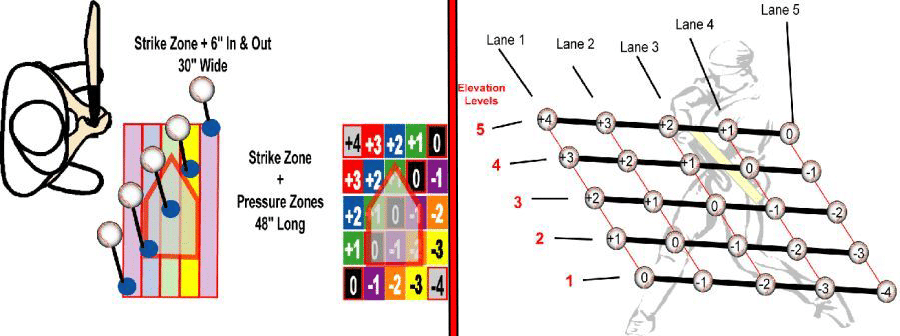
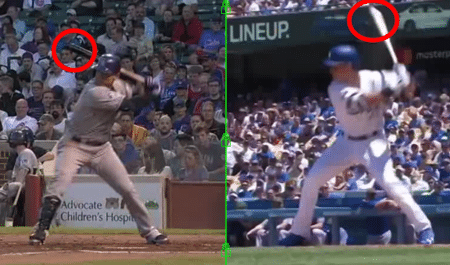
“Pluses” take-away from hitter’s reaction time, “minuses” add to hitter’s reaction time (images are pitcher’s POV). Photos courtesy: HittingIsAGuess.com
The one thing I like about Perry Husband’s contribution to hitting a baseball is he goes by “data, not feelings”.
He’s made a science out of a hitter’s reaction time. Perry Husband has accumulated, “Over 10 years of study and testing of amateur hitters and two years of intense study of major league at bats in a 4 million plus pitch database”. At his site Effective Velocity, Perry Husband explains his Effective Velocity system for pitchers:
“The Downright Filthy Pitching Series is a very in depth study of speed as it relates to the hitter’s reaction time. Initial velocity is the speed of the ball as the radar gun sees it, perceived velocity is the speed of the ball as the mind’s eye sees it and Effective Velocity is the speed it actually is. Effective Velocity (EV) is the initial velocity plus the location effects of the pitch due to different locations having different reaction times…A 90 MPH pitch can and does equal many different speeds, depending on where the pitch is located. “
His data (photo above) suggests that a hitter has to be quicker to pitches up in the zone, and in. And pitches down in the zone and away, give a hitter more time to adjust. Perry Husband reports from his findings:
“Did you know that the highest exit velocities off Major League hitters’ bats come off the pitches in the lowest part of the strike zone? How about that the most homeruns hit are off pitches at the very bottom of the strike zone as well?”
Over the past year, I’ve softened to some of Perry’s hitting a baseball mechanics. His information is vital to understanding if…
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
90-Degree Barrel Angle to the Spine Rule NOT True?

Giancarlo Stanton: 90-degree barrel to spine rule. Note: outside pitch slightly up in zone. Photo courtesy: MLB.com
CLICK HERE for the post that explains this Rule. The preceding post link refers to the barrel, not the front arm to spine angle. There are FOUR ways a hitter gets to pitches at the top/bottom of the strike-zone, and/or inside/outside of the plate…
- Tilting at the waist with the upper body (the lower the pitch, the more the tilt),
- Back knee bend,
- Front knee bend, AND
- Barrel path.
Another reader got upset saying that I’m teaching two different swings. And enlightened me about his extensive study into the brain, and that taking a bent arm from the initiation of the swing and changing the shape to straight is impossible for the brain to do. Click Here for a conversation Perry and I had on the arm bar.
Remember, Perry Husband said that the highest ball exit speeds and home-runs were off of lower pitches? Do you think it could be because the front arm was able to extend at impact? Creating a longer lever and allowing for a smooth transfer of bat speed (angular velocity) into ball exit speed (inertial force). These are fundamental rules in the Conservation of Angular Momentum.
Look, if our goal as coaches is to get hitters 100% on-time, 100% swing effective, then we must take a serious look at the front arm bar. High exit velocity is key to batted ball distance, and without it Launch Angles alone won’t score more runs. Besides, how many commercial and/or passenger airplanes get off the ground without high horizontal velocity? CLICK HERE for an interview we did with Perry Husband about his system.
One last thing to look into hitting a baseball…
University of Miami Study: The Biomechanics of the Baseball Swing
Major shout out to one of my readers and local lesson parents, Nieszka, for bringing this to my attention. This study was done by Dr. David Fortenbaugh at the University of Miami (CLICK HERE if you want to download the 200+ page pdf). Here’s the gist of how the study was put together:
- Study Objective: to compare swings against pitches thrown to different locations and at different speeds.
- AA-level Minor League Baseball players (n=43) took extended rounds of batting practice in an indoor laboratory against a pitcher throwing a mixture of fastballs and changeups.
- An eight camera motion analysis system and two force plates recording at 300 Hz captured the biomechanical
data. - The swing was divided into six phases (stance, stride, coiling, swing initiation, swing acceleration, and follow-through) by five key events (lead foot off, lead foot down, weight shift commitment, maximum front foot vertical ground reaction force, and bat ball contact).
- Twenty-eight kinematic measurements and six ground reaction force measurements were computed based on the marker and force plate data, and all were assessed throughout the phases.
The findings?
According to the Study:
“A large number of biomechanical differences were seen among the swings against various pitch locations. More fully rotated positions, particularly of the pelvis and bat were critical to the batters’ successes on inside pitches while less rotated positions keyed successes against outside pitches. The trail and lead arms worked together as part of a closed chain to drive the hand path. Successful swings had the trail elbow extended more for HIGH IN and flexed more for LOW OUT, though batters often struggled to execute this movement properly. A distinct pattern among successful swings against fastballs, successful swings against changeups, and unsuccessful swings against changeups was witnessed; namely a progressive delay in which the batter prematurely initiated the events of the kinetic chain, especially when unsuccessful in hitting a changeup.”
Hitting a Baseball Conclusion
So, let’s tie up everything we talked about in hitting a baseball…
On pitches low and/or away, the hitter has more reaction time (Perry Husband research), so tilting at the waist (on lower pitches) and extending the front elbow to impact is key (90-degree barrel spine rule). And because the outside and lower pitches will be hit slightly deeper than inside and higher pitches, the trailing elbow will have more bend in it at impact (Miami Study).
There can be a harmonious relationship between an arm bar, and consistency getting to pitches up and in the zone. CLICK HERE for this post that gets into the different “catcher’s gloves” on how to do this. HINT: it has to do with the “belly button” catcher’s glove.
Readers, I want to hear your thoughts on hitting a baseball in the Comments below…