Learn how to increase bat speed and power by hitting the ball better, farther, and harder using this baseball or softball drill. Discover how in this Buster Posey swing experiment, breakdown, and analysis.
Buster Posey Swing Breakdown Experiment: ADD 6-mph To Bat Speed Not ALL In The Hips?
Question: Is Increased Bat Speed ALL in the Hips?
Using the Zepp (Labs) Baseball app, I wanted to use the Scientific Method to analyze whether Buster Posey’s hips OR spinal mechanics is what increases bat speed.
Background Research
Most elite hitting instructors, pros, and Hall of Famers think it’s ALL in the hips. The “it” is a mystery even to them. It shouldn’t be this way. When we look at proven human movement science, we find that just firing the hips isn’t good enough. My question to those people is, what about the piece of hardware above the pelvis, attaching it to the shoulders – the spine?
Before getting into the experiment and analyzing Buster Posey’s swing, we need to lay ground work first. Watch this THREE videos first:
- Miguel Cabrera and the timing of torque.
- Josh Donaldson v. Jose Bautista: how spine engine mechanics are amplified by Gravitational Forces, and
- Adrian Gonzalez: how-to naturally spring load the body.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
Hypothesis
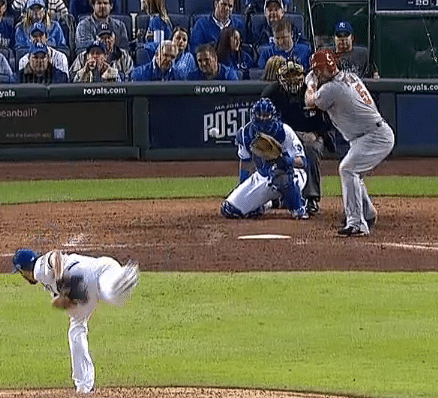
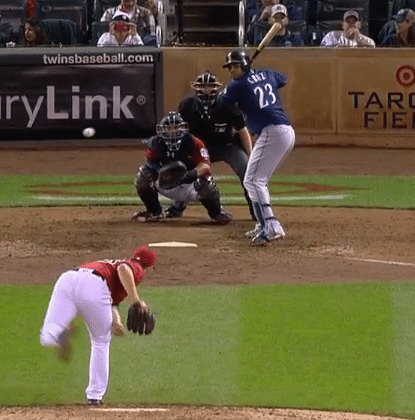
Albert Pujols NOT showing his numbers like he could. Definite hip hinge (tilt) towards the plate. Photo courtesy: MLB.com
Based primarily on my research and study of Dr. Serge Gracovetsky’s book The Spinal Engine, and Thomas Myers’s book Anatomy Trains
, I believe a hitter like Buster Posey, that shows the pitcher their numbers – while keeping the hips in neutral – creates the separation (or spinal torque) needed before landing to produce natural friction-free repeatable power.
Rather than just focusing on the hips to go first, and the front shoulder to stay on the pitcher. In the experiment, for the sake of brevity, I’ll differentiate between the two with “showing numbers” or “NOT showing numbers”.
Buster Posey: Not ALL in the Hips Experiment
Equipment Used:
- Zepp Baseball app,
- ATEC Tuffy Batting Tee,
- Rawlings Official NCAA Baseballs,
- Two yellow dimple baseballs (feedback markers),
- Flip Video Camera and Tripod, and
- 33 inch, 30 ounce Pinnacle Bamboo bat.
Setup:
- Yellow dimple ball feedback markers = my bat length, plus two baseballs
- Distance from plate = end of the bat touching inside corner of plate, and knob of bat touching my mid-thigh
- Tee was set one baseball’s length behind the front feedback marker, and tee height was about mid-thigh
- Forward momentum was eliminated in this experiment, and I hit from a 1-2 second pause at landing
- First 100 baseballs hit was “NOT showing numbers”, focusing on hips first, and front shoulder pointing at the pitcher at landing
- Second 100 baseballs hit was “showing numbers”, focusing on showing numbers, slight down shoulder angle, and hiding the hands
- There was about 30-45 minute break between both Buster Posey Experiments
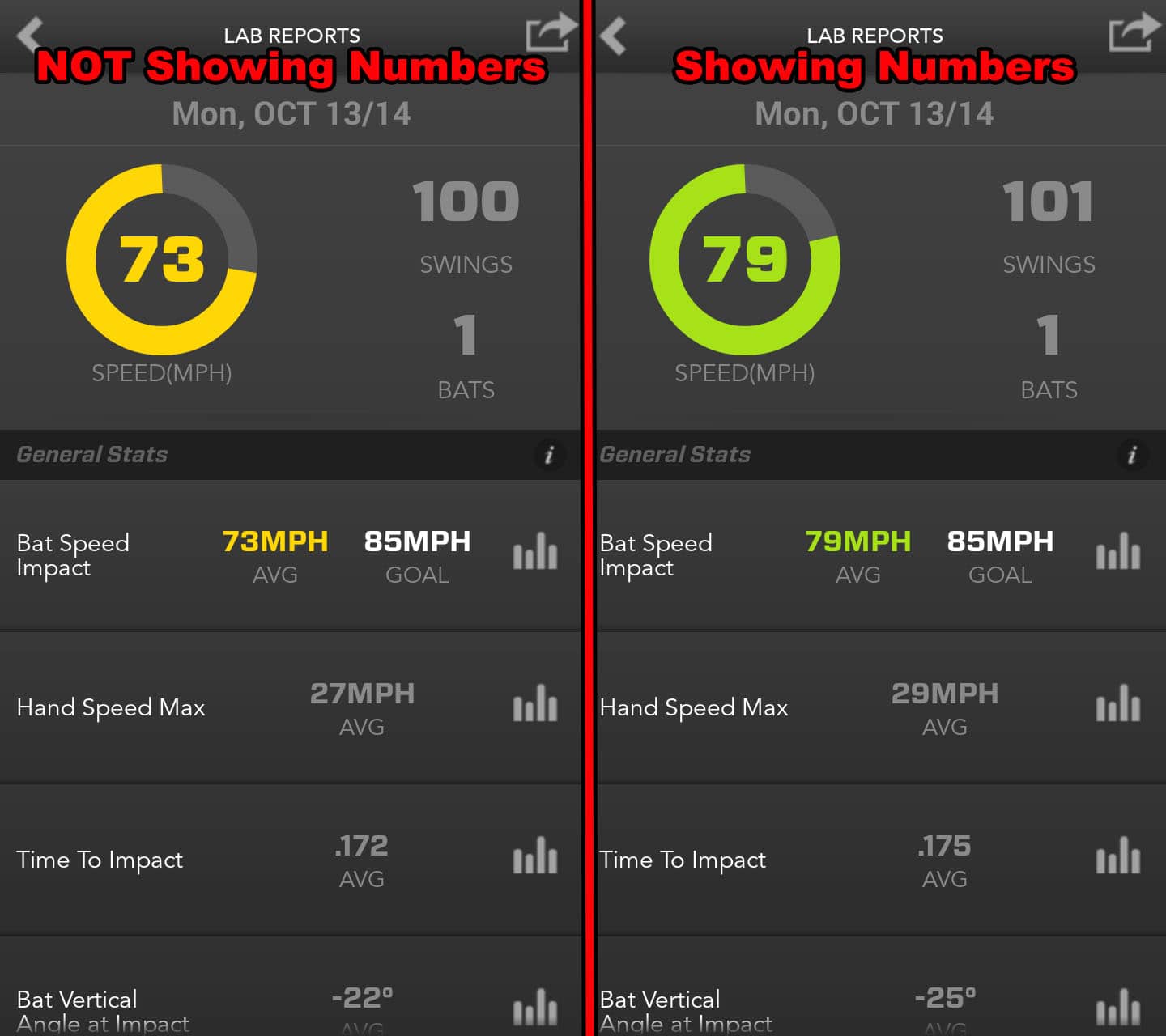
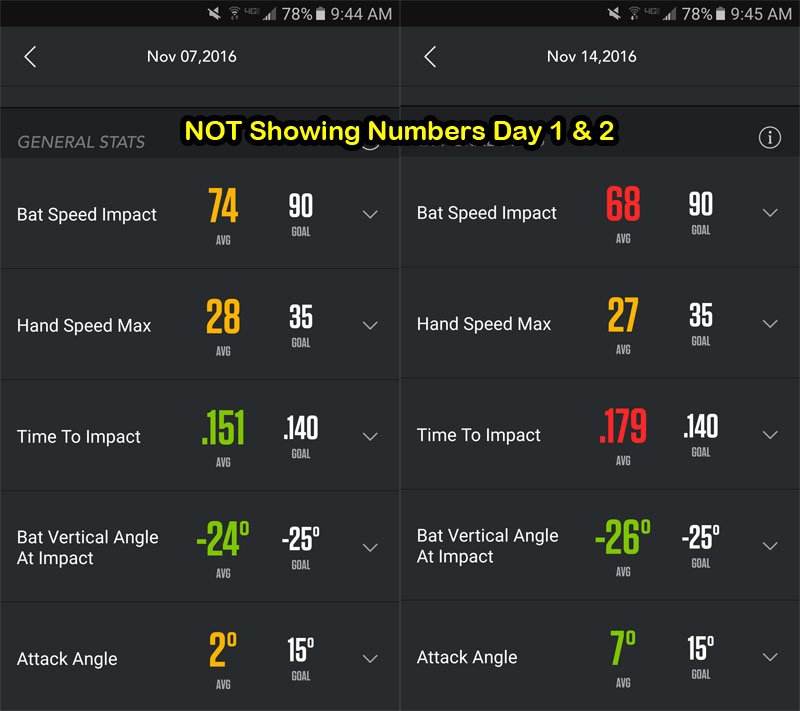
Data Collected (Zepp Baseball App):
Data Analysis & Conclusion
- Average bat speed for NOT showing numbers at landing: 73-mph
- Average bat speed for showing numbers at landing: 79-mph (+6-mph)
- Highest bat speed for NOT showing numbers at landing: 82-mph
- Highest bat speed for showing numbers at landing: 88-mph (+6-mph)
- Hand speed max for NOT showing numbers was: 27-mph
- Hand speed max for showing numbers was: 29-mph (+2-mph)
As you can clearly see, “NOT showing numbers” puts a hitter at a clear repeatable power DISADVANTAGE.
Notes

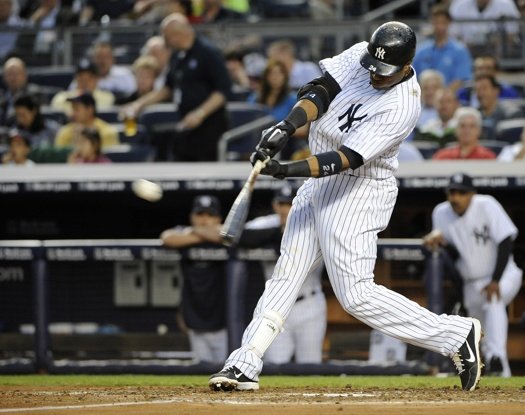
Andrew McCutchen: showing numbers, slight down shoulder angle, hiding hands, hip hinge (tilt) towards the plate. 2013 NL MVP. 3rd in MLB OPS in 2014. All 5’10”, 190 pounds of him! Photo courtesy of MLB.com.
- I don’t go out and take 200 swings in a given day, so I was getting fatigued by the time I got to the last hundred swings (“showing numbers”) part of the experiment. Goes to show this isn’t about muscles, but connective tissue.
- Remember, I purposely eliminated forward momentum from the Buster Posey Experiment because I wanted to reveal how “showing the numbers” can effect a hitter’s bat speed. CLICK HERE to see the results of a Forward Momentum Experiment I did using the Zepp Baseball App.
- “Showing the numbers” IS NOT adding more rotational ground to make up during the Final Turn. It’s a natural way of super-charging connective tissue over muscles.
- A slight bend at the waist (hip hinge) towards the plate – before landing – improves efficiency, not detracts from it. Just look at Posey, McCutchen, and Pujols pictured hitting home-runs in this post. This is how an athlete takes the slack out of the posterior chain (calves, hamstrings, butt, and back). ALL shapes and sizes use it.
- During NOT showing the numbers, I felt like I had to guide my hands more. It took more effort to extend through the ball instead of rotating off (rolling over), than with showing the numbers.
- Make sure when “showing the numbers”, the hitter isn’t losing sight of the incoming pitch with the back eye.
- Also, make sure when using a slight down shoulder angle that the head stays in-line with the spine. The angle is slight, about five to ten-degrees.
The Bottom Line?
When we analyze hitters like Buster Posey, we NEED to hold our analysis to a higher standard. Proven human movement science. We have to go away from mechanical fixes based on “feelings”. The “Oh, I’ve been working on this and it seems to work”, isn’t good enough. Neither is, “Ted Williams said so!” Or, “I watch 25-hours of high level hitting footage in a day, so listen to me.” That stuff DOES NOT matter. Science does. I want to see the data, NOT listen to feelings. The heavy lifting has been done for us. It’s up to us to apply it.

![Buster Posey VIDEO: Not ALL In The Hips [Experiment]](https://hittingperformancelab.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/buster-posey-showing-number-compare.png)