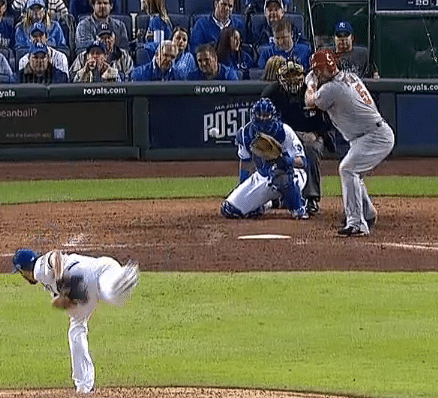
Discover how to increase bat speed and improve hitting power with these tee drills for baseball and softball youth players as young as 8 years old.
“Blocking” Like Jose Bautista: A Baseball Hitting Drills For Bat Speed Experiment
Question: Does Landing Bent with the Front Knee & then Straightening it, Add Bat Speed?
Using the Zepp (Labs) Baseball app, I wanted to use the Scientific Method to analyze if “Blocking”, or using Ground Reaction Forces (GRF), produces a significant gain in bat speed.
Background Research
Check out this YouTube video from ZenoLink about “Blocking”, or GRF:
CLICK HERE for a Wikipedia article defining Ground Reaction Forces. Quote from post:
“The use of the word reaction derives from Newton’s third law, which essentially states that if a force, called action, acts upon a body, then an equal and opposite force, called reaction, must act upon another body. The force exerted by the ground is conventionally referred to as the reaction, although, since the distinction between action and reaction is completely arbitrary, the expression ground action would be, in principle, equally acceptable.”
CLICK HERE for another baseball hitting drills for bat speed post I did about Edwin Encarnacion: A How-To “Blocking” Guide.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
Hypothesis
Based on the above baseball hitting drills for bat speed research and study, I think “Bent Knee Blocking” will produce more bat speed than “Straight Knee Blocking”. For some of you, this may be obvious. But the data comparing the two is quite interesting to see.
Baseball Hitting Drills For Bat Speed Experiment: “Blocking”
Equipment Used:
- Zepp Baseball app
,
- SwingAway MVP Bryce Harper model,
- Two yellow dimple baseballs (feedback markers),
- Flip Video Camera
and Tripod, and
- 33 inch, 30 ounce Pinnacle Bamboo bat.
Setup:
- Yellow dimple ball feedback markers = my bat length, plus two baseballs
- Distance from plate = end of the bat touching inside corner of plate, and knob of bat touching my mid-thigh.
- SwingAway was set slightly behind the front feedback marker, and ball height was about the hip.
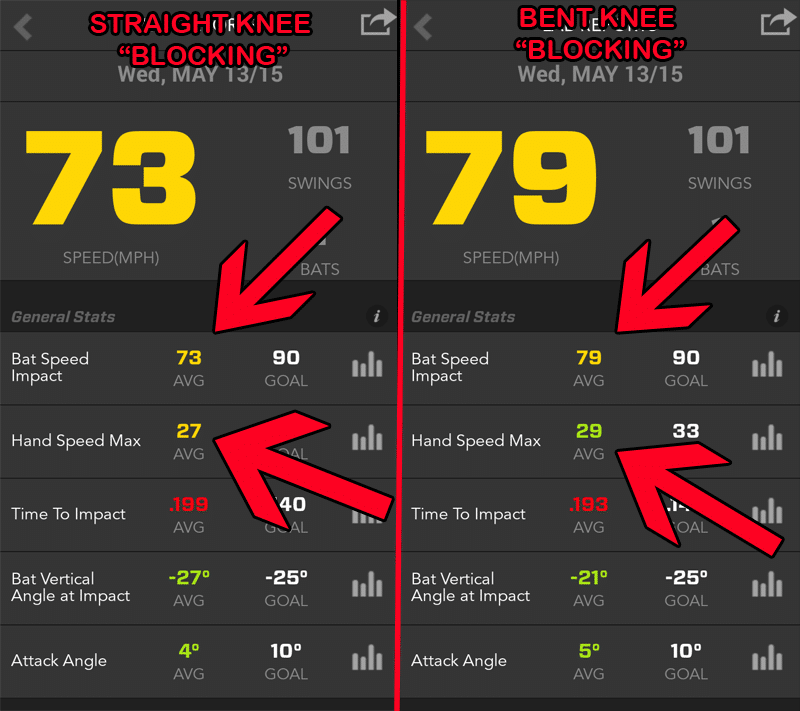
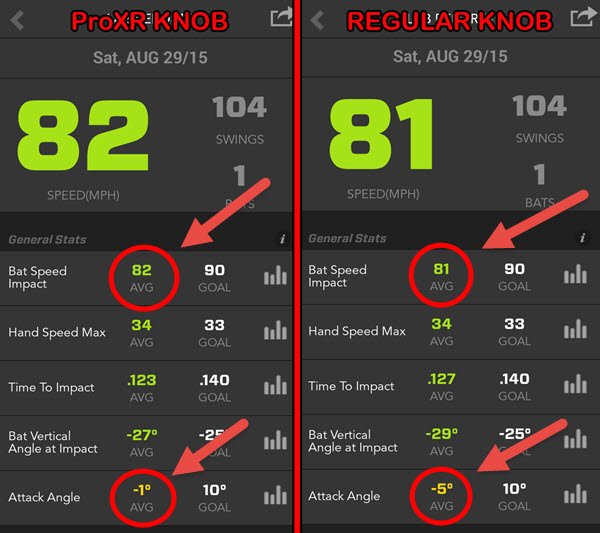
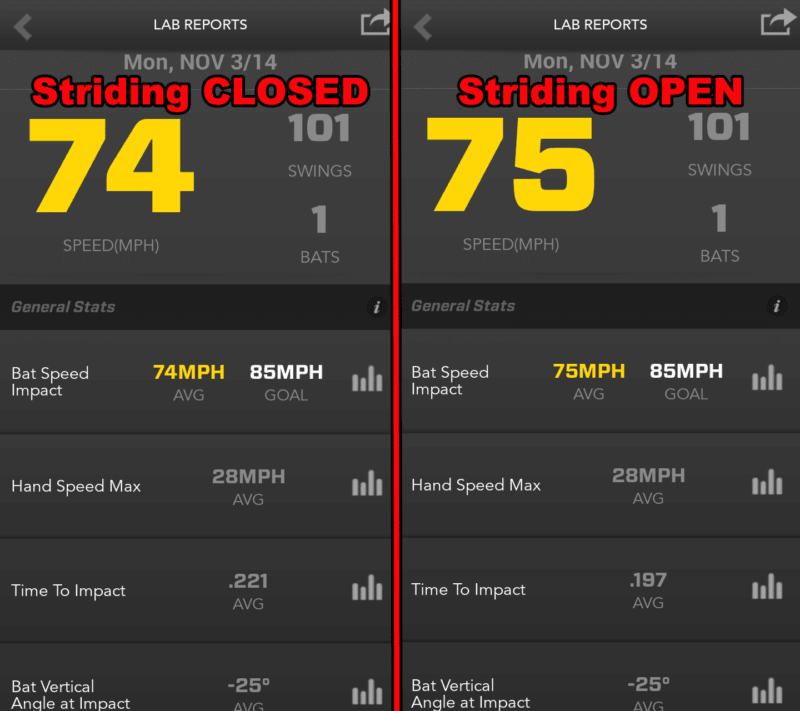
- First 101 baseballs were hit with a landing leg angle of about 170-degrees.
- Second 101 baseballs were hit with a landing leg angle of about 146-degrees.
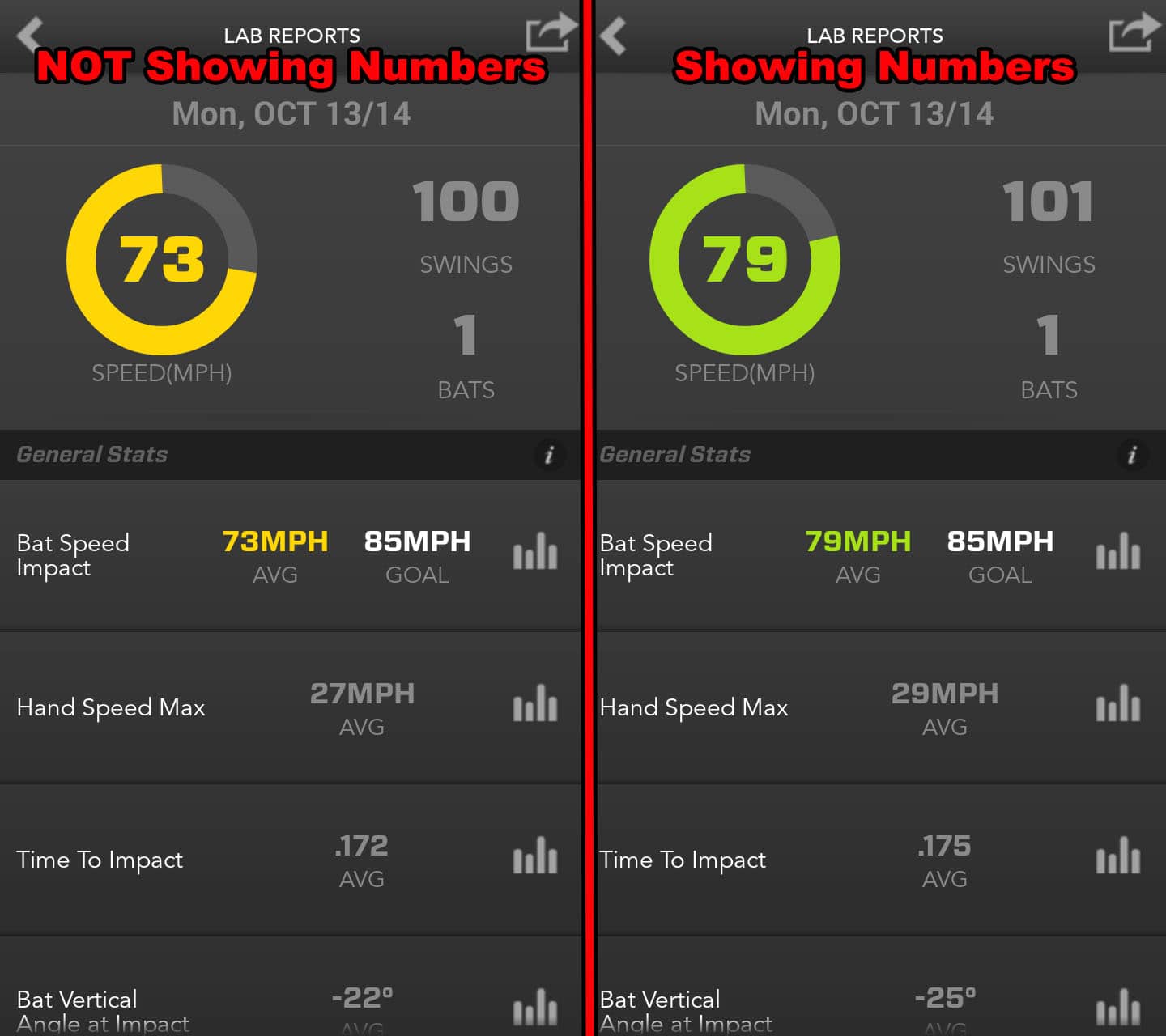
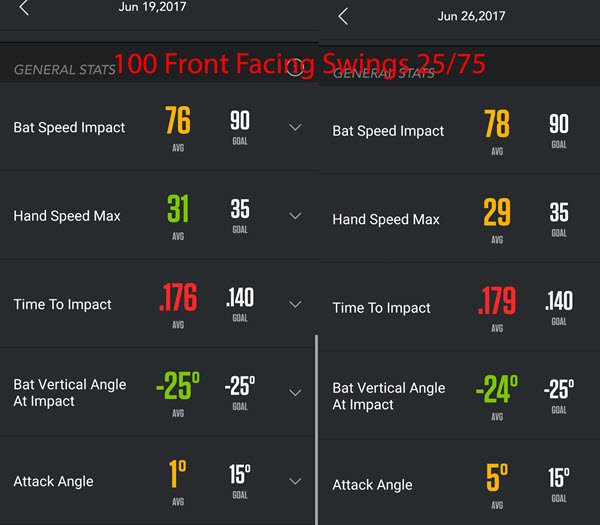
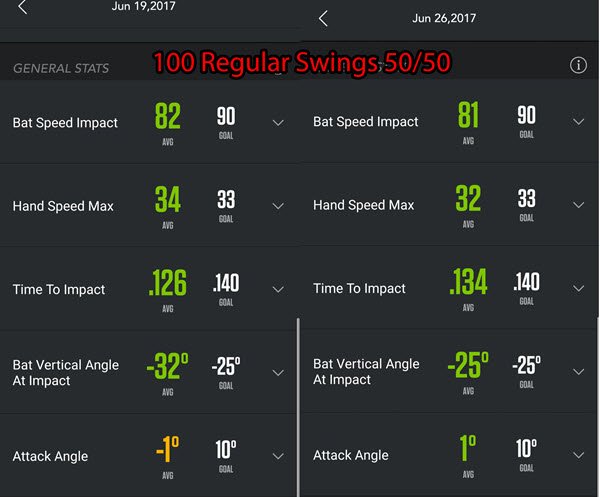
Data Collected (Zepp Baseball App Screenshots):
Data Analysis & Conclusion
- 6-mph average bat speed difference between “Straight Knee Blocking” versus “Bent Knee Blocking”,
- 2-mph average hand speed difference between “Straight Knee Blocking” versus “Bent Knee Blocking”,
- The Average Time to Impact was about the same,
- The average Bat Vertical Angle at Impact had a 6-degree difference, and
- There was only 1-degree of difference between the Attack Angles.
Notes
- I broke my swing into two steps (stopping momentum), to make sure I could accurately isolate the difference in the front knee action.
- The “Bent Knee Blocking” 6-mph average increase is equivalent to 24-48 feet of batted ball distance (depends on the speed of the pitch).
- What was interesting was the huge shift in Bat Vertical Angle at Impact. I suspect it’s because of the higher landing position, and the barrel compensated down to accommodate hitting the sweet spot.
- Looking at the nominal increase in Attack Angle and the wide degree shift in Bat Vertical Angle at Impact, it looks like “Straight Knee Blocking” would lead to more mishits.
- Like in this “Blocking” Experiment, baseball hitting drills for bat speed need to be put to the test. We can’t just feel something will increase bat speed. We must look at what the data says.
In Conclusion
From the Baseball Hitting Drills for Bat Speed Experiment data, we can see that “Bent Knee Blocking” produces more average bat and hand speed than “Straight Knee Blocking”. The other thing that landing with a bent knee does (approx. 146-degrees), is shrink the strike-zone. Or at least create an illusion that it’s shrinking, to the umpire. I call this “Getting Shorter”.
Coupled with forward momentum, the hitter is making a “cut”, much like a wide receiver would on an “L” route. Except instead of the wide receiver changing from the Sagittal (forward/backward) to the Frontal (sideways) Plane of motion, the hitter changes from the Frontal to Transverse (twisting) Plane of motion. And in order to do this, the “plant leg” needs to be bent in order to transfer Ground Reaction Forces efficiently. You’ll NEVER see an NFL wide receiver “cut” with a straight plant leg…they plant bent, then push into the ground to change directions.














![Buster Posey VIDEO: Not ALL In The Hips [Experiment]](https://hittingperformancelab.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/buster-posey-showing-number-compare.png)