Learn how to improve youth mental game toughness skills training for baseball or softball players using a fixed vs growth mindset psychology by Dr. Carol Dweck…
A Fixed Mindset May Be Dangerous To Your Hitters

Fixed versus Growth Mindset illustration photo courtesy: KaylaCelliott.com
Nothing is more frustrating – and disappointing – than running into a Fixed Mindset coach…
All you get are excuses…excuses…EXCUSES!!
Think about the Fixed and Growth Mindsets, from Dr. Carol Dweck’s book Mindset , like the operating system for your computer or mobile device. Each Mindset (or operating system) will take you down a different path to problem solving.
, like the operating system for your computer or mobile device. Each Mindset (or operating system) will take you down a different path to problem solving.
Some may say, well, the examples you give are reveal “closed minded coaches”, not a Fixed Mindset. I disagree.
Look, I’m sure at times there are some closed minded Growth Mindset coaches, but I’m willing to bet my first born on that there are exponentially more closed minded Fixed Mindset coaches. You see, closed mindedness is a subset of a Fixed Mindset coach, NOT a Growth Mindset one.
Before I get into taking you through the story, I wanted to let you know what I have for you:
- An 8-min, 25-sec video from Trevor Ragan outlining the difference between a Fixed v. Growth Mindset (video above)
- Address 7 DEVASTATING Fixed Mindset coaching EXCUSES that are killing the progress of smaller power hitters, and
- The Fixed versus Growth Mindset Introduction from my new book.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
Back to the story…
I ran into a couple of them on social media this past week about the promise I make in my Catapult Loading System book: How To Teach 100-Pound Hitters To Consistently Drive The Ball 300-Feet.
Particularly, they were commenting that Hudson White, the hitter I covered in this blog post, weighing 130-pounds hitting the ball 398-feet – and that includes wood – was an over-exaggeration.
To their credit, they did concede it’s possible. But then oh man, here came ALL the excuses, taking credit away from the hitter’s dedication to his craft…
- “The bat was hot”,
- “Isn’t the norm, or has athletic ability – I wouldn’t take credit for that”,
- “Average kids don’t use there body’s efficiently as someone with above average athleticism can regardless of training”,
- “Only in batting practice and not in games”,
- “130-pound hitter wouldn’t make our Varsity team”,
- “Working with the exception, not the rule”, and the kicker comment about hitting ground-balls…
“I’ve never played or coached this game from a text book or a state sheet and never will. I do just what I’m doing here, I talk shop with knowledgeable people. Scouts, college coaches, minor league players and coaches and once in a blue moon with hitting instructors. I have very rarely come across any one of them that is as passionate about getting the ball in the air so much. Most of them try to keep things as simple as possible, which means barrel the ball, hit it hard. Period. No emphasis on air v ground, just barrel it.”
Addressing Excuse #1
Hudson White has hit balls over 398-feet with a Hickory wood. My over half a dozen hitters tripling their body-weight in batted ball distance (i.e. 100-pounder hitting ball 300-feet), are not using hot bats, and neither did Hudson at the National Power Showcase Home-Run Derby Competition put on my Brian Domenico at the Texas Rangers ballpark in Arlington in 2016.
Addressing Excuses #2 &3
What does athleticism mean exactly? What are your rules that say one kid is athletic and another is not? I’d hallucinate yours are different than mine. However, the question is, can we make a seemingly nonathletic kid average or even above average athletically? Not all, but I think we can make EVERY kid move better. And next week’s post interview with the founder of the Bosu Ball, David Weck, will shine more light on how to do this.
I brought up examples of Michael Jordan, Tim Tebow, and one of the best cricket players in the world weren’t able to or currently are not doing well enough to make it to the Big League level. It can be argued these are non-baseball athletic examples, but you’re saying above average athletic ability is one of the main causes for young hitters tripling their body-weight in batted ball distance. It’s speculation.
I’d argue “train-ability”, as referenced in the Heritage Study from David Epstein’s book The Sports Gene: Inside the Science of Extraordinary Athletic Performance , as a more crucial element than above average athleticism in explaining why my hitters (and other coaches’) can triple their body-weight in batted ball distance. Learning is learning, but they still have to learn the most effective mechanics.
, as a more crucial element than above average athleticism in explaining why my hitters (and other coaches’) can triple their body-weight in batted ball distance. Learning is learning, but they still have to learn the most effective mechanics.
Take for instance my 67-pound hitter blasting a 180-foot dinger – in a game – after working with me for 6-months. When we first started he couldn’t hit his way out of a wet paper bag. So in 6-months did he auto-magically go from below average to above average athletically?
Addressing Excuse #4
I have game footage film of two of my hitters tripling their body-weight in batted ball distance:
By the way, Temo now is around 135-lbs and is consistently driving the ball 370+ feet. Also, Hudson White is driving the ball 400-feet in games as well.
Addressing Excuse #5
Are you KIDDING ME!? To write a player off based on the “eye test” is ignorant. It makes me sad how many of these “under-weighted” young hitters are not being given a chance because some coach DOESN’T HAVE A CLUE how to get educated in all things effective.
Coach, if this is you, then you’re going to love the Introduction to my book that follows, on Growth v. Fixed Mindsets…
But first,
Addressing Excuse #6
This one made me laugh. I responded back with something like, man I must be running into all these exceptions then! Myself and the hundreds of coaches – who’re getting the same, if not better, results than I am by the way – teaching the same system, must be exception magnets!!! lol
Addressing Bonus Excuse #7
Look I agree, line drives and barreling the ball AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE should be every coaches objective for their hitters. However, the question is raised, if you were to have your hitters miss, would you rather have them miss hit the ball in the air or on the ground? I’m not going dive deep into this here, because I did that already in the Ground-Ball Rant, but I do want to say High School coaches (on down) are getting a false sense of achievement with the ground-ball because fielders aren’t what they are at the D1 and Pro levels.
Now, listen closely…
If you’re not teaching your hitters to consistently drive the ball (in the air), then YOU WILL HAMSTRING them at the higher levels, if they make it that far. And by then, it’s too late.
I was just on the Coaching Minds Podcast by host Justin Lewis (Please follow him on Twitter @The_Coach_Mind), our interview I’ll be posting in 3 weeks or so, shared that he works almost exclusively with High School and College level fast-pitch hitters.
The horror stories he revealed the new hitters he’d get in college, reported they were only taught to slap the ball their whole life because of how “tiny” they were. What happens to these girls at the college level? When a hitting situation would come up to drive in runs, you know what the college coach does to these “tiny” slap hitting specialist?
They pinch hit them.
If ground-balls were so great, then why not let this slapping specialist slap?! Ground-balls are her specialty!! Let me give you a clue, ground-balls work less at the college level…and EVEN LESS at the Pro level. Don’t let this happen to your hitters.
And after hearing ALL these excuses, it was refreshing to get this email message from a coach after watching my webinar (I can’t say he uses my system though, but the message speaks for itself):
“The 135-lb pound kid…that is good but not that impressive…not too many kids at the age of 12 and 13 that weigh 135 pounds…he should be hitting the ball that far…now the 67 pound kid…that is impressive (one of my players at 75 pounds can hit the ball 225)” – ulley13usparks (username)
Now, he was talking about my two 13u hitters Eddie S. and Temo C. both weighing 135-lbs and driving the ball 370+ feet, and my 67-lb hitter I spoke of earlier in this post. “…should be hitting the ball that far…”, man, how refreshing to hear.
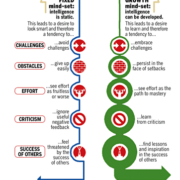
This leads me to the MAIN ISSUE…the above excuses are from Fixed Mindset coaches. The video above is fantastic education on the Fixed versus Growth Mindset debate in under 10-minutes. Rest assured you’ll be a more effective coach after watching the video. And if you like the video, then you’ll love Dr. Carol Dweck’s book Mindset .
.
And to drive the nail home, below I’m including the Introduction to my new book The Catapult Loading System: How To Train 100-Pound Hitters To Consistently Drive The Ball 300-Feet, that people are loving by the way…just read the Amazon book reviews so far.
Without further adieu, here’s the Fixed v. Growth Mindset Intro…
—–
“In times of change, learners inherit the earth, while the learned find themselves beautifully equipped to deal with a world that no longer exists.”
– Eric Hoffe
FREE Online Bat Speed Hitting Program Access?
Try our online bat speed hitting training program Risk Free built for baseball and softball hitting enthusiasts like you. 30-Day Risk FREE Trial for LIMITED TIME only.
Click Button Below to choose the best remote learning plan for you...
YES! I Want To Choose My Plan
Fixed Versus Growth Mindset Coaching
When it comes building consistently powerful hitters, this book will provide you with the pathway to get there.
However, I think the most important aspect to bridging the gap between what the coach teaches and what the player absorbs has to do with Mindset…
Coaches can be split up into two groups.
- Fixed Mindset
- Growth Mindset.
According to Dr. Carol Dweck, in her bestselling book Mindset: The New Psychology of Success,
“In a fixed mindset, people believe their basic qualities, like their intelligence or talent, are simply fixed traits. They spend their time documenting their intelligence or talent instead of developing them. They also believe that talent alone creates success—without effort.”
Here are some things you hear FIXED Mindset coaches saying,
- You can’t teach a Little Leaguer to hit like a Major Leaguer because they aren’t strong enough.
- Hand speed can’t be coached.
- Natural hitters are just born.
- Hitting is subjective and is different for everybody.
- The greatest hitters just have great hand-eye coordination.
- That 12u 100-pound hitter can consistently hit the ball 300-feet because they’re hitting with a HOT bat.
- He/She can hit the ball hard and far because of their body mass.
All of those are to the contrary of Dr. Dweck’s definition of a Growth Mindset coach:
“In a growth mindset, people believe that their most basic abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. Brains and talent are just the starting point. This view creates a love of learning and a resilience that is essential for great accomplishment.”
These coaches find a way. They ask the right questions. They ask, “Why not?” They don’t rest on elite-level playing experience or decades of coaching experience.
The objective of a Growth Mindset coach is to learn principles first, or “rules”. Then, design methods to stay within those lines, not the other way around. You’ll learn more about this in CHAPTER 1.
I’ll let Billy Murray give Growth Mindset coaches a word of caution in dealing with Fixed Mindset coaches on social media:
“It’s hard to win an argument with a smart person, but it’s damn near impossible to win an argument with a stupid person.”
Why?
From Henry Ford:
“If you think you can do a thing or think you can’t do a thing, then you’re right.”
One puts the forest before the trees (versus missing the forest for the trees), and the other is swatting a piñata with one eye blindfolded!
I get it, we all want to be heard and validated as being knowledgeable in a subject, but high credibility in the wrong place is highly misleading.
Some go to extreme lengths to IMMEDIATELY make their presence known. Here are some Fixed Mindset saying tip-offs:
- “I’ve played [X-number] years professionally and I should know.”
- “I’ve been coaching for 30+ years, and this is why you should listen to me.”
- “I’ve studied millions of hours of video analysis of only the best hitters. I know what I’m talking about”
- “I’ve put a lot of work into the cages, and that’s how I know what I’m talking about”
Don’t get me wrong, the last two points above have their place and CAN be effective in learning and seeing success patterns, BUT massive effort going in the wrong direction can be gross negligence.
Besides, it takes A LOT of effort in the cages and hours of video analysis to stumble onto the right answers. But, I have a more elegant solution that will dramatically cut your learning time in half!
You’ll know what to look for, so you can SUPERCHARGE your time in the cages and also for when you’re doing video analysis. You’ll read about this in CHAPTER 2.
Willful ignorance.
I heard this term on Facebook and love it! People online defend their hitting philosophy and theories to the death, even if human-movement principles validated by science, reveal the opposite.
I mentally play the “What if…Strip” game with Fixed Mindset coaches…
WHAT IF this person NEVER…
- Played in the Big Leagues…
- Coached for 30+ years…
- Studied millions of hours of video…
- Put a lot of work into the cages…
…IF we stripped them of their primary credibility indicator, THEN I ask:
- What do they actually know?
- Who or what have they studied? (Physics, Bio-Mechanical, Psychology, Exercise Science sources? Not baseball or softball)
- What kind of consistent or inconsistent results do they get with their hitters?
We’ll get deeper into the Credibility Fallacy in CHAPTER 3.
Fixed Mindset coaches are stuck. They regurgitate the same information they’ve been taught in the past without question. They may even say their hitting philosophy is a science, but it’s not. It’s a pseudo-science. Their copy and duct-taped together hitting philosophy reeks of uncertainty. We’ll get more into that in CHAPTER 4.
Here’s one of my favorite quotes by Dan Farnsworth:
“Doing a thing and understanding a thing do not automatically qualify you to teach a thing.”
And it’s so true!
I can tell with 100% confidence that I have not:
- Played Professional baseball,
- Coached for over 30 years,
- Studied millions of hours of only the best hitters on video, or
- Put in as much work in the cages as others say they do…
So, why listen to me?
Because of:
- What I actually know,
- Who and what I’ve studied, and
- The results my hitters are getting.
We’ll drill deeper into these points in the following CHAPTERS, but what I think is VERY IMPORTANT for those who never played ball past Little League or 12u softball,
…That you too, can be a hitting expert.
All you need is a passionate curiosity to learn and apply the human-movement principles that are validated by science, to hitting a softball or baseball. I’m going to teach you how to conduct fool-proof swing experiments, so that you can use your findings to show people who won’t take you seriously.
You’ll learn my swing-experiment-blueprint in CHAPTER 4.
And I’m going to break it down for you, so don’t worry if you didn’t do well in science class back in school.
CHAPTER 5 will take you through the science of springy fascia and spinal-engine-mechanics. This is the WHY behind the methods we discuss in the later chapters. You can skip this one, but please return to it later, so you have ammunition for Fixed Mindset coaches who won’t believe the results your hitters are getting.
CHAPTERS 6 through 11 will take you through the practical methods and drills my hitters are using to consistently triple, or at least double, their body-weight in batted ball distance.
Lastly, CHAPTER 12 will walk you through, how to train these newly-learned hitting techniques. I believe the training is as important, if not more critical, than the mechanics you’ll be learning in this book.
I had a third-year pro-hitter drive up from San Diego (about a 7-hour drive for me, one-way), comment that he thought the training by itself was worth the trip! And he spent a fortune in time and money to work through a whole weekend with me.
What You’ll Learn
Here’s what you’re going to learn in the upcoming pages:
- Why hitting philosophy fails and principles that are validated by science succeed.
- Why you shouldn’t make video analysis FIRST-priority, when modeling elite hitters.
- What 30+ year coaching experience and pro players won’t tell you, and how the information source you focus on can dramatically cut down your learning curve.
- How to become a hitting expert when you’ve never played higher than Little League.
- There’s a BIG advantage to learning how the body actually loads (and it’s not what you’re thinking).
- A simple method that helped Babe Ruth to consistently crush the ball with some of the heaviest bats ever used.
- Elite-hitters revealing ways to hit balls with High-Exit-Speeds, swing after swing, using three elements even a 4-year-old can understand.
- At last, the secret to transitioning grooved batting practice swings into game at-bats is revealed.
WHY is this Important to you now?
There are four reasons…
Most “hitting stuff” we’ve learned is DEAD WRONG. It’s based off philosophy and theory, and with the technology available today, we can test the value of those hitting philosophies.
Nowadays, everyone is a hitting “expert”. How do we differentiate between an effective versus an ineffective approach? This is important because it’s not how PRO someone is, how many years of coaching they’ve accumulated, how many man-hours of video analysis they’ve done, or even how many hours of lessons they do in a given day. You can’t argue with science and powerfully consistent results.
“Confusion” between mechanical causation equaling correlation. Can you put backspin on a ball by swinging down on it (i.e. negative barrel Attack Angle)? Yes, you can. But, will the hitter consistently get the ball in the air that way? No. In this case, swinging down does not consistently put the ball in the air with authority, and IS NOT what the best are REALLY doing on slow motion video.
Big difference between what’s “real” and what’s “feel”. When Mike Trout says he works at ‘getting on top of the ball’, that doesn’t mean Johnny’s coach should go out and share with his team this method. In fact, Mike Trout says this to himself to protect his swing from HIS naturally tendency to upper cut too much, like he says to ‘chicken wing’. The cues that MLB and professional hitters use are often lost in translation with the younger-end user.
Is the Information in this Book for you?
First, we WILL NOT be talking about:
- ‘Squishing bugs’,
- ‘Swinging down on the ball’, OR
- ‘Loading & exploding the hips’.
Second, this is specifically about how to apply human movement ‘rules’ to hitting a moving ball, and not about hitting ‘philosophies’ or ‘theories’ that DO NOT predictably work in LIVE case studies.
Third, the information in this book is based on the success my personal hitters have had both online and locally, plus the hundreds of coaches, who’ve duplicated the results, if not bettered them by using this system.
The House Rules
Here’s what I’m not promising…
- No “get powerful hits, quick”.
- No “do nothing, and crush the ball”.
- My results aren’t remotely typical.
- Most people who buy ANY “consistent-power-swing” training, will not have success with getting consistent power in their hitters.
Addressing point numbers one and two above…
Some of my 12-years-old and under hitters, weighing around 100-pounds, don’t start consistently driving the ball 300-feet right away. Some take 2.5 years to get to consistency, whereas before they do it “every once in awhile”. Other hitters, although rare, achieve this in less than 6-months. This seems to be the range for the hitters I work with.
It depends on work ethic and what David Epstein calls ‘learn-ability’, in his book, The Sports Gene: Inside the Science of Extraordinary Athletic Performance.
Addressing point numbers three and four above…
I encourage my hitters to work hard on the things we go over, and to keep on trying even after hitting major obstacles.
Most young hitters don’t do that. They just show up for a lesson or gather information and “get ready” to work…or they throw in the towel and quit at the first bump in the road.
It took a lot of hard work for my hitters to start seeing favorable hitting outcomes.
Interestingly, it was the work with my hitters that gave me the inspiration to write this book.
The bottom line is, I have no idea what your results may or may not be.
And it’s not my place to try to predict that. Your success is up to you, as always.
Onward…
—–
CLICK HERE to order your copy of The Catapult Loading System on Amazon today…
FREE Online Bat Speed Hitting Program Access?
Try our online bat speed hitting training program Risk Free built for baseball and softball hitting enthusiasts like you. 30-Day Risk FREE Trial for LIMITED TIME only.
Click Button Below to choose the best remote learning plan for you...
YES! I Want To Choose My Plan