Discover how to increase baseball and softball bat speed (slow pitch too!), improve ball exit velocity, whip, and power. Learn in this Miguel Cabrera hitting breakdown how to teach even a little league 8 year old kid to swing the bat faster…
Miguel Cabrera REVEALS Timing Of Torque
The third installment to the Hitting Backwards: 4 Common Mistakes Hitters Make video series, stars 8-time All-Star & 2-Time AL MVP Miguel Cabrera. I’ll show you how hitting instructors get torque timing wrong, causing reciprocal inhibition to occur in reverse.
In this Miguel Cabrera video, we’ll look at:
- Why walking mechanics hold the key to repeatable power,
- Whether we should land front foot closed or open? And
- Why the timing of torque is important.
Thanks to Bob Hall from Canada for the subject of this video blog article.
SCIENCE-BASED TRAINING:
Improve your hitting strategy dramatically by applying human movement principles.
Learn not only how and what to train but also the science behind the methods.
Walking Mechanics: Key to Repeatable Power?
The following “compression signal” sequence is according to Dr. Serge Gracovetsky’s spine engine mechanics:
- Left front leg heel strike – compression signal travels up the leg into the pelvis telling it to open to the right,
- The signal continues up the spine into the shoulders, telling them to counter-rotate (left), and
- This is why your opposite arm and leg come forward at the same time.

Photo courtesy: WalkezStore.com
Land Front Foot Closed OR Open?

Photo courtesy: OnMilwaukee.com
Big guys like Barry Bonds and Miguel Cabrera land closed (less than 45-degrees). Small guys such as Ryan Braun and Jose Bautista tend to land open (more than 45-degrees). Which way is the right way?
4 reasons to keep the front toe open (minimum of 45-degree angle):
- Joint Connection – Toe closed? So is knee and pelvis. The compression signal travels fast after heel strike, so pelvis must be in neutral (or parallel to the plate) in order to open without friction,
- NO Separation – If toe, knee, and pelvis are closed after compression signal, then front shoulder has to compensate by flying open the same time as the pelvis. This doesn’t engage our elastic energy systems.
- Compensation is Inevitable – We find the closed toe in hitters like Barry Bonds and Miguel Cabrera just end up peeling or jumping open anyway at or shortly after contact. So why not get the toe out of the way to begin with?
- Pitchers Land Open – And also if you look at Olympic Throwers and Shot Putters, they all land open before they throw or “put” their objects.
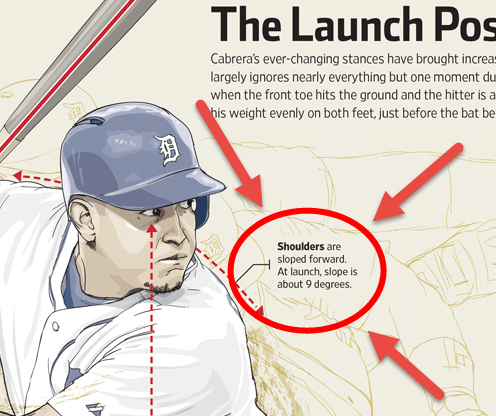
Why the Timing of Torque is IMPORTANT

Photo courtesy: OttawaLife.com
Torque timing in the swing, also known as shoulder-pelvis separation, is often cued wrong. Instructors often yell, “Fire the Hips!” In high level swing mechanics, we find the hips (or pelvis) does fire first. But, the timing coaches cue on is all wrong. Shoulder-pelvis separation occurs before the front heel touches down, NOT after.
If you missed the following parts to the Hitting Backwards: 4 Common Mistakes Hitters Make video series:
- CLICK HERE for Common Mistake #1 featuring Ryan Braun
- CLICK HERE for Common Mistake #2 featuring Adrian Gonzalez
Stay tuned for Common Mistake #4, where we debunk whether the friction-free swing is pushing or pulling the backside through…